iOS响应链中HitTest、nextReponder的介绍
iOS的UIEvent事件有好几种:Touch Events(触摸事件)、Motion Events(运动事件)、Remote Events(远程事件),其中最常用的应该就是Touch Events了,今天我们主要就讲它,核心就是到
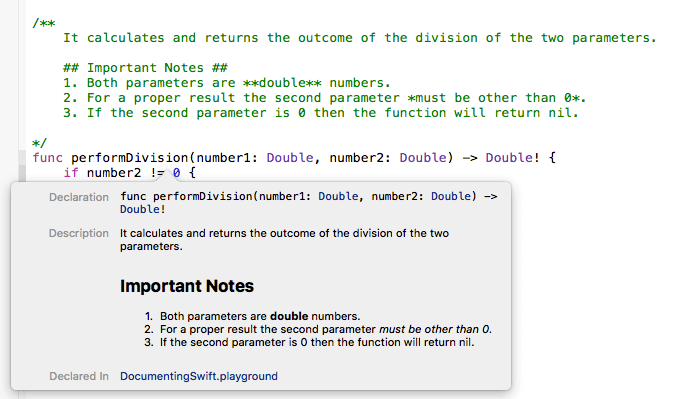
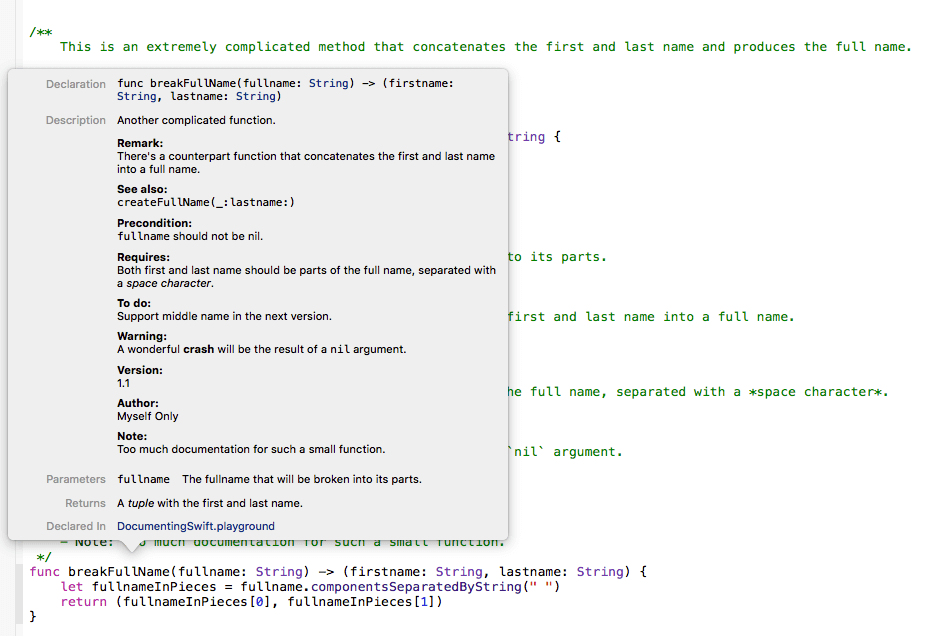
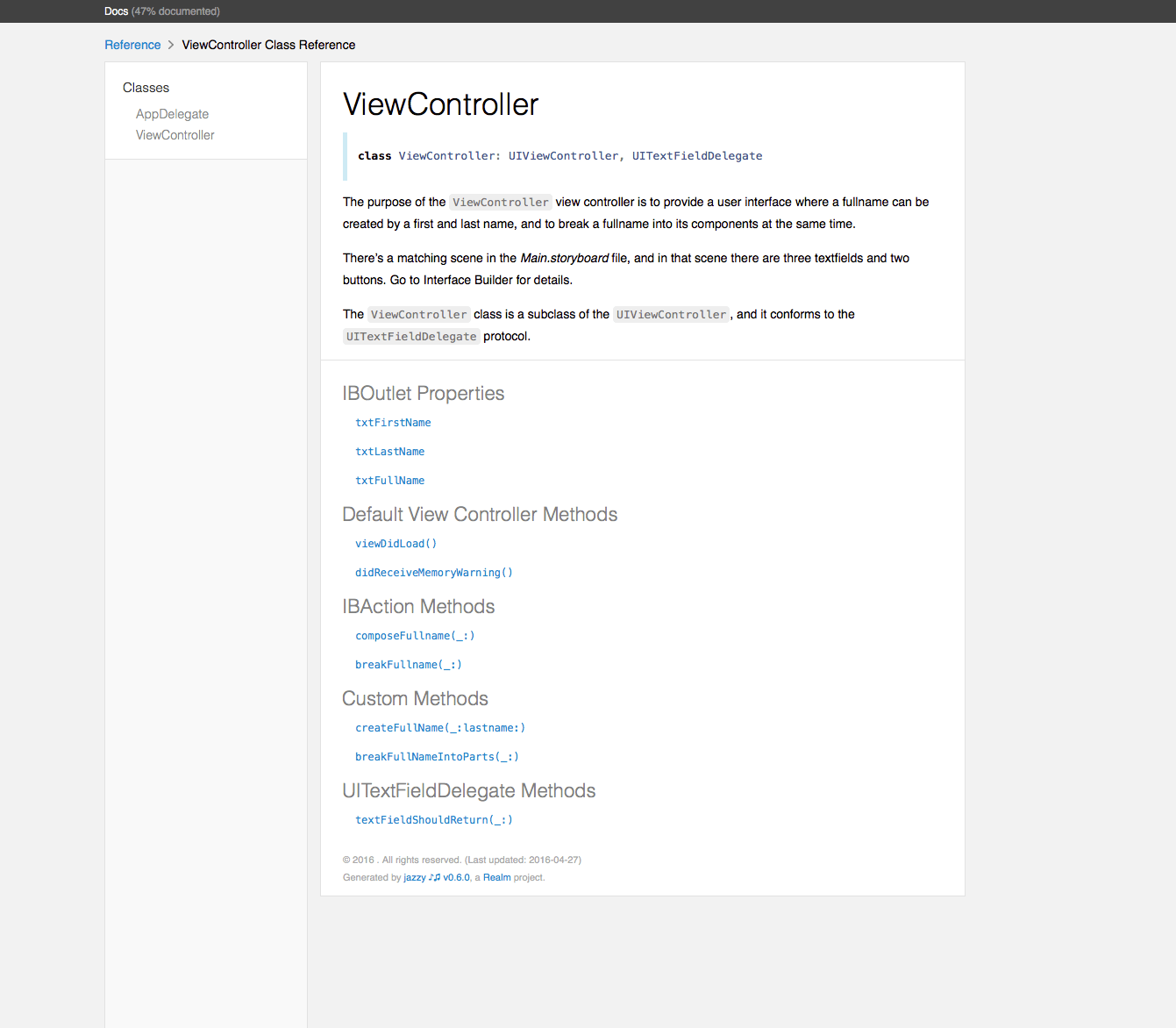
UIView的func hitTest(_ point: CGPoint, with event: UIEvent?) -> UIView?
以及nextReponder两个
比如成果:魔图&图片浏览 复杂的视图层级拆分


考一考: 直接继承于UIResponder的类有哪些?
UIResponder ?? 响应链 ??
- 响应链是什么时候怎样构建的?
- 事件第一个响应者是怎么确定的?
- 事件第一个响应者确定后,系统是怎样传递事件的?
响应链的构建
先看看UIResponder类
|
|
常见的触摸响应链构建
- addSubview
- ViewController 初始化

事件响应过程
- 触摸开始
- 事件入栈
- runloop响应
- uiapplication 事件传递给 windows
- hitTest 找到 view (hitTest会被调用两次,为什么,不知道?)
- hitView 响应 touchEvent
核心的方法
|
|
注意:hittest & pointinside是uiview的实例方法
比如tableview的cell点击,hitTest寻找响应cell的过程
- windows
- windows.rootController (navController).view
- navController.rootControler (vc).view
- tableview
- some cell
- contentView
Note: 查询过程也不是这么顺利的,有弯路,也有属性限制
- hittest打算从后往前遍历subviews,直到找到才停止遍历
- subview必须符合
- pointInside return YES
- 属性限制有
- alpha > 0.01
- hidden == NO
- userInteractionEnabled == YES
|
|
那我们干预后,HitTest的实战应用就有
- 复杂的视图层级的拆分
|
|
- 自定义Touch事件传递对象
|
|
- 自定义控件的响应区域及响应层级
view修改响应区域方式有两种,一种如下,它的superview来hitTest,第二种自己hitTest
|
|
响应链 .nextResponder
和 hitTest自底向上相反,它是从最末端的responder向下传递,hitTest自下而上查找响应的view,nextResponder是基于hitTest基础上,自上而下寻找event的响应者
常见的应用案例:BPUIResponderAdditions中的方法,可以查找view的Controller或navigationController
|
|
知识点:
- 响应链事件传递
通过nextResponder向下传递event
演示
touchesBegan / super.touchesBegan 或 nextResponder.touchesBegan 一直调用下去
- 第一响应者
有拦腰截断的意思,原有的顶部第一响应者被修改,响应链中接收事件第一人(常见textField,webView及UImenuController,见demo)
演示
- Button event 先下传递
- becomeFirstResponder后,nextResponder无事件下传
- canBecomeFirstResponder \ becomeFirstResponder 拦截
- cancelsTouchesInView
系统会将Touch cancel消息发送给hitTestView ,并调用hitTestView的TouchCancel
演示
demo:button的touchUpInside对UIPanGestureRecognizer的影响